Animal and plant cell: differences
The animal and plant cells are eukaryotic cells , that is, they are cells that have a nucleus unlike prokaryotes that do not have a nucleus or most organelles ( you can find the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells in this post ).
However, despite being both eukaryotes, they have very clear differences, such as that the plant cell has chloroplasts and a cell wall and the animal cell does not. But these are not the only differences, but there are some more that we will explain in detail below.
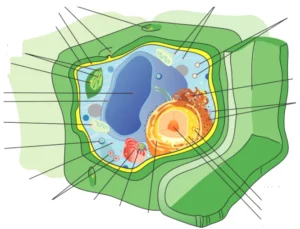
The animal cell is found in animals as it is very easily understood by its name, but also in protozoa and amoebae which are unicellular organisms. The plant cell is found in plants and algae.
To study the difference between animal and plant cells, we are going to group the different aspects into these three groups:
- Structure and composition of cells
- Nutrition
- Cell division (mitosis and meiosis)
Differences between plant and animal cells in cell structure and composition
The differences that we can find in terms of composition and structure are fundamentally based on the absence and presence of organelles according to the type of cell (animal or plant), and in some cases also on the composition of some organelles or structures such as the cell membrane. .
Organs and structures unique to the plant cell
Cell wall
The plant Eukaryotic cells have cell wall while animal cells do not.
The cell wall is mainly made up of cellulose that surrounds the cell like an exoskeleton, giving it rigidity and supporting osmotic forces.
Vacuoles
The c élulas animals some exceptions have no vacuoles while plant cells do have them . They fulfill the function of storing reserve substances, sap, dyes, poisons and also waste substances.
They also shape the plant cell by helping to maintain its shape and the turgor of the plant cell, which is vital for it to perform its functions (more on turgor in this post on osmosis in plant cells ). The set of vacuoles of the plant cell is called a vacuome and can reach 90%.
Chloroplasts
Plant cells have chloroplasts while animal cells do not. Chloroplasts are the place in the plant cell where photosynthesis takes place.
Chloroplasts are similar to mitochondria. They are organelles surrounded by a double membrane with invaginations towards the interior that form branches called lamellae. Thylakoids are found in lamellae, which are sacs where chlorophyll is found, which is the pigment that allows photosynthesis to be carried out.
Glioxisomes
The glyoxisomes peroxisome are a type found in the plant cell especially in storage tissues such as seed lipid.
They are a special type of peroxisome because their function is to mobilize and transform the lipids accumulated in the reserve tissues of the seed into carbohydrates that can be used in germination. The metabolic reactions that carry out this conversion are called the glyoxylate cycle that do not occur in the animal cell.
Plasmodesmata
The plasmodesmata are also absent in the animal cell and present in the plant . They are fine cytoplasmic ducts that cross the cell wall to allow molecules to pass directly from one cell to another. This happens because a plasmodesmus of a plant cell is in continuity with that of the neighboring cell.
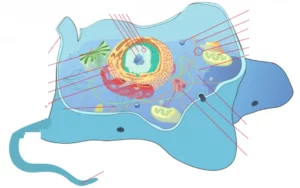
Organs unique to the animal cell
Centrioles and centrosome
Another difference between the animal and plant cells, which in this case is also characteristic of the animal cell, is that the animal cell has centrioles and the plant cell does not. Likewise, the centrosome is formed by the centrioles so it is not found in the plant cell either.
The centrioles play the role of forming the chromatic spindle during mitosis and meiosis and, in addition, they are the organelle from which the cilia and flagella are formed. In plant cells the presence of cilia and flagella is not very frequent except in some algae and male gametes, while in animal cells it is more frequent.
On the other hand, it is possible to wonder what happens with mitosis in plant cells if they do not have centrioles,… how is the mitotic spindle formed? In this case, it is formed from microtubule organizing centers and is called anastral spindle . One difference between the mitotic and anastral spindles is that the anastrales are not as well positioned at the poles as in the case of the mitotic spindle.
Plant cilia and flagella are formed from the basal body, which has the same structure as the centrioles.
Lysosomes
The lysosomes are only found in animal cells . They are membrane-enclosed vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes capable of digesting substances and therefore it is where intracellular digestions take place.
Difference in the composition of some organelles
Cellular membrane
Cell membranes usually contain sterols that are responsible for maintaining properties such as maintaining the exact fluidity of the membrane and structure, vital for the survival of the cell. In the cell membrane of animal cells, the sterol that carries out this function is cholesterol . In plant cells they are sterols of another type.
Mitochondria
Plant mitochondria can oxidize exogenous NADH and many are relatively insensitive to cyanide. You can find more about mitochondria here.
Plant and animal cell nutrition
Nutrition type
With regard to the difference in nutrition of animal and plant cells, reference is made to the energy substrate they use, that is, where they obtain energy.
Animal cells are heterotrophic , that is, they obtain energy from organic compounds from other living beings while plant cells are autotrophic , that is, they are capable of obtaining energy from sunlight and inorganic compounds thanks to the realization of photosynthesis.
Reserve molecules
Plant cells store carbohydrates in the form of starch whereas animal cells store carbohydrates in glycogen molecules .
Cell division or cytokinesis
In this section we refer specifically to the separation into two cells once mitosis and meiosis have taken place. This process is called cytokinesis.
In the animal cell, cytokinesis is produced by a constriction of the cytoplasm, by the action of actin and myosin proteins, dividing the cell in two.
In the plant cell, cell division (or separation) occurs because a partition is built in the middle of the cell called the fragmoplast from which the cell wall that will divide the cell in two will be formed. The fragmoplast is formed from vesicles of the Golgi apparatus that contain elements of the cell wall.
Table of differences between animal and plant cells
Here is a detailed summary table with the differences between plant and animal cells:
| DIFFERENCES IN STRUCTURE AND COMPOSITION | ANIMAL CELL | PLANT CELL |
| CELLULAR WALL | NO | YES |
| PLASMODESMOS | NO | YES |
| CELLULAR MEMBRANE | YES (with cholesterol) | YES (without cholesterol) |
| NUCLEUS | YES | YES |
| MITOCHONDRIA | YES | YES |
| CHLOROPLASTS | NO | YES |
| ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM | YES | YES |
| GOLGI APPARATUS | YES | YES |
| CENTRALS | YES | NO |
| RIBOSOMES | YES | YES |
| COWS | NO (only some exceptions) | YES |
| PEROXISOMES | YES | YES |
| GLIOXISOMES | NO | YES |
| LYSOSOMES | YES | no |
| FLAGELOS AND CILIOS | YES | NO (Only in algae and gametes) |
| CENTROSOME | YES | NO |
| NUTRITION DIFFERENCES | ||
| NUTRITION | Heterotrophic | Autotrophic |
| RESERVE MOLECULE | Glycogen | Starch |
| DIFFERENCES IN THE CELLULAR DIVISION | ||
| CELL DIVISION (CYTOKINESIS) | Yes by a contractile ring of actin and myosin | Yes with the creation of the fragmoplast |